GNSS signals are received from satellites about 20,000 km away. Since GNSS uses noise-level, low-power signals to calculate its position, they can easily be disrupted by RF disturbances. For instance, the ICD (Interface Control Documents) and C/A (Coarse/Acquisition) codes for the L1 signal used in the civilian bands are open source, making it possible to generate deceptive signals.
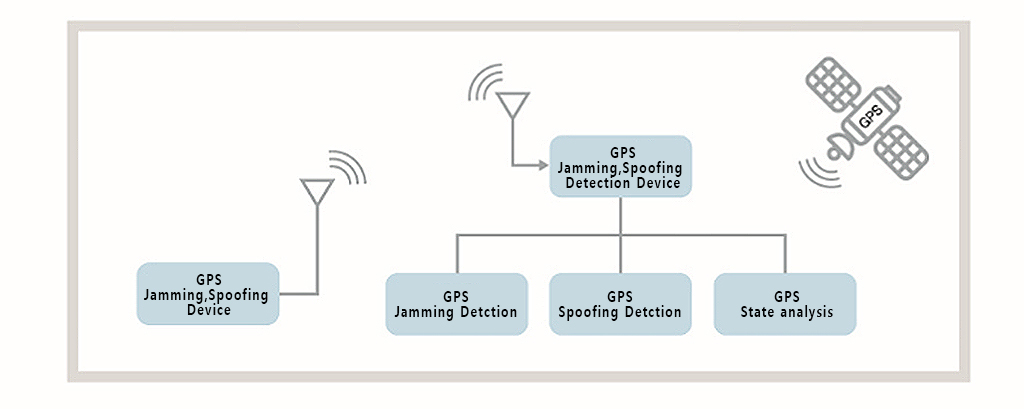
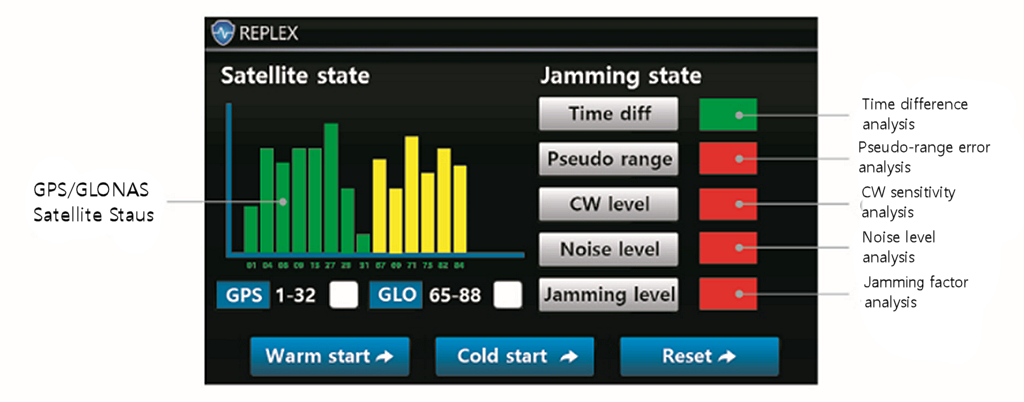
GNSS spoofing signal detector is a device that can receive and analyze signals from GNSS jammers/spoofers to indicate whether a GNSS signal is being jammed or deceived. In addition to simple signal strength analysis, it is also possible to detect sophisticated deceptive signals by comparing, in a comprehensive way, pseudo-ranges, CW sensitivities, and visual differences.
- GPS jamming prevention technology to detect the sophisticated deceptive signals
- GPS RINEX information grinding for time/ position error detection
- Individual GPS satellite signal analysis to identify deception
- Analysis of pseudo-range, CW sensitivity and noise comparison to discriminate disturbance and deception
- GPS and GLONASS satellite signal analysis